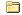
int pix1 = videofeed1.pixels[ videofeed1.width * y + x ];
Check out the
Images and Pixels article in the learning section for more information about how to use pixels[] arrays.
Check the demos that come with Processing, eg
Examples > Libraries > Video (capture) > BrightnessThresholding
I've written a template for accessing two camera feeds (though haven't tested it beyond compiling, since my system doesn't like / work with the QuickTime capture used by Processing!)
-spxl
Code:/**
* spxlDuelingCameras
* http://subpxiels.com
*
* PLEASE NOTE: this code uses the same index into the
* pixels[] arrays for BOTH cameras and the OUTPUT window,
* which is assuming they are all the same size (eg 320x240).
* If you want to use different sized camera frames or a
* different-sized output window, you will need to calculate the
* pixels[] array offsets separately or you will end up with a
* big mess (if not an out of bounds exception if you try to
* read past the end of one of the smaller arrays).
*
* Updated: 2010-02-07 by subpixel
* - Use w,h variables in call to size().
* - Use width and height for main loops instead of cam1.width
* and cam1.height
* - Fixed code for setting p2,r2,g2,b2
*/
import processing.video.*;
Capture cam1;
Capture cam2;
void setup()
{
// Start with simple case where both
// cameras produce the same frame size
int w = 320;
int h = 240;
int fps = 30;
size(w, h, P2D);
frameRate(fps); // desired OUTPUT frame rate
try
{
String[] camNames = Capture.list();
println("Camera names: \n" + camNames);
println("Initialising: " + camNames[0]);
cam1 = new Capture(this, w, h, camNames[0], fps);
println("Initialising: " + camNames[1]);
cam2 = new Capture(this, w, h, camNames[1], fps);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
println("Error attaching camera(s): " + e.getMessage());
exit();
}
}
// This just updates the Capture object
// with the new frame when it is available
public void captureEvent(Capture c)
{
c.read();
}
public void draw()
{
loadPixels(); // For OUTPUT window's pixels[] array
for (int i=0, y=0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++, i++)
{
// Pixel from cam1 (red, green, blue)
int p1 = cam1.pixels[i];
int r1 = (p1 >>> 16) & 0xff;
int g1 = (p1 >>> 8) & 0xff;
int b1 = p1 & 0xff;
// Pixel from cam2 (red, green, blue)
int p2 = cam2.pixels[i];
int r2 = (p2 >>> 16) & 0xff;
int g2 = (p2 >>> 8) & 0xff;
int b2 = p2 & 0xff;
// Information available:
// - current (x,y) coordinates
// - current pixels[] array(s) index
// - pixel value from each camera
// at the current (x,y) cooordinates
// - red, green, blue component colour values
// for pixels from each camera
// (Very!) simple example: average r,g,b values
int r = (r1 + r2) / 2;
int g = (g1 + g2) / 2;
int b = (b1 + b2) / 2;
// "Safety" code
r = constrain(r, 0, 255);
g = constrain(g, 0, 255);
b = constrain(b, 0, 255);
// Recombine r,g,b into integer pixel value
int p = (r << 16) | (g << 8) | b;
pixels[i] = p; // OUTPUT window's pixels[] array
}
}
updatePixels(); // OUTPUT window's pixels[] array
}

 Pages: 1
Pages: 1